|
Click Here for a "How-To" guide on creating Contour Grids
The Misc tab controls a few miscellaneous gridding options including the user-specific grid file directory, seismic shot point decimation, the preview window, grid scaling and grid templates.
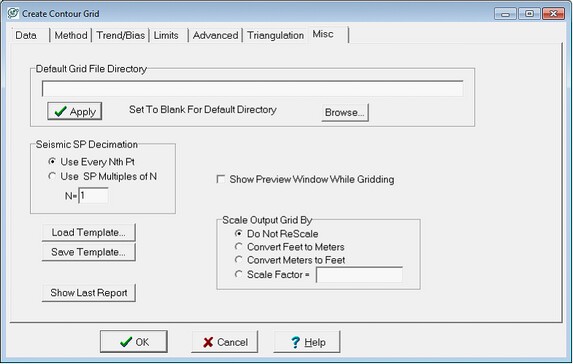
Default Grid File Directory
By default, Petra stores all grids into a single GRIDS folder inside the projects directory. Particularly in large projects with multiple interpreters, its sometimes useful to designate multiple grid folders. Changing this setting just affects the individual user, and not the default grid file of the project as a whole.
Seismic SP Decimation
A single seismic survey can contain far too many points to usefully grid. Its often useful to thin seismic data coverage down to accelerate gridding. This option only disregards data during gridding, and does not erase any seismic data.
Use every Nth Pt This option decimates data points just by occurrence, where Petra will use every Nth point and disregard the rest. Setting the N value to 5 will start with the first available SP point, such as SP 7, 12, 17, 22, etc.
Use SP Multiples of N This option decimates data points with a little more control over which specific SP points are selected. Setting the N value to 5 ensures that Petra will use SP 0, 5, 10, 15, etc.
Show Preview Window While Gridding
This option simply adds a preview window to the normal gridding screen. During gridding, this preview shows a small thumbnail of the grid as its created. This is particularly useful for early QC of large, time-consuming gridding processes.
Scale Output Grid By
This option provides a way to quickly rescale grids. This is particularly useful for rescaling grids based in feet to meters and vice versa. In a project where depths are stored as feet, selecting the Convert Feet To Meters option before gridding will multiply all values in the grid by 0.3048, for example.
Gridding Templates
A template saves all the settings associated with creating a grid file in a *.gt file. Loading this template restores these settings. This can be particularly useful in a an iterative environment where several grids are being updated and modified continuously.
|