Log Image Editing |
|
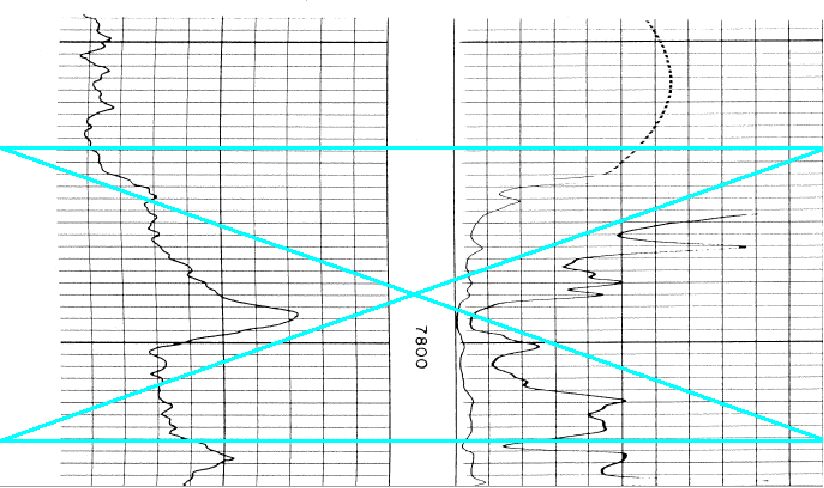
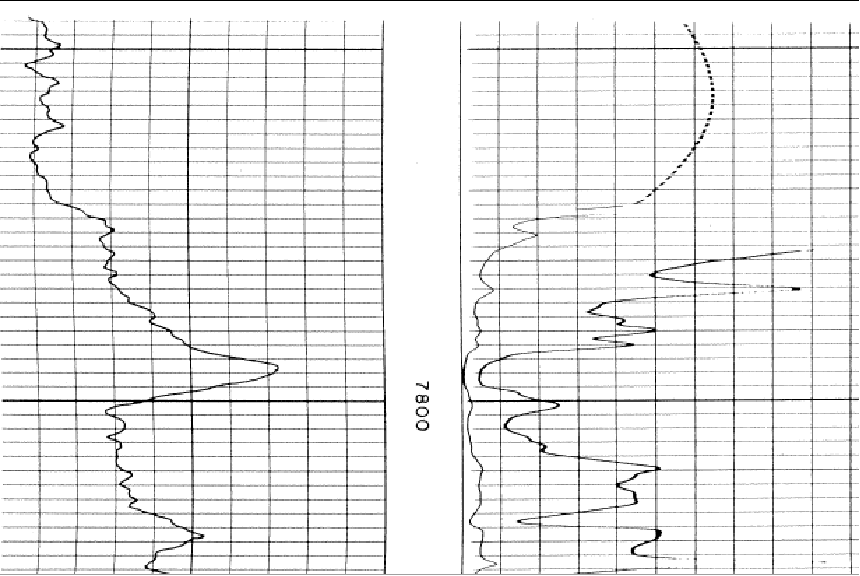
The Log Calibration tool includes a few additional tools for editing the raw log image files. This process modifies your image file, so be sure not to save over the original image file and have a backup. To restore the filtered lines select File>Reload Original Image. This can be useful for cleaning up images for digitizing raster logs. Since the tracing algorithm looks for adjacent dark pixels, it can easily get confused by vertical scale lines and horizontal depth lines. The Log Calibration tool can filter out straight horizontal and vertical lines that can confuse the auto-digitzing function. Log imaging editing isn't foolproof - using filters can reduce the clarity of the curves as well, especially where the curves intersect the filtered horizontal or vertical lines. Rotate ImageScanning can sometimes subtly rotate image logs. The easiest way to spot this is tilted depth/scale lines or by zooming out. Note that this can increase the margins to the left or right the actual image. It's often useful to use the "Crop at Edges" can remove extra white space created by rotating the image. To use this tool, select the
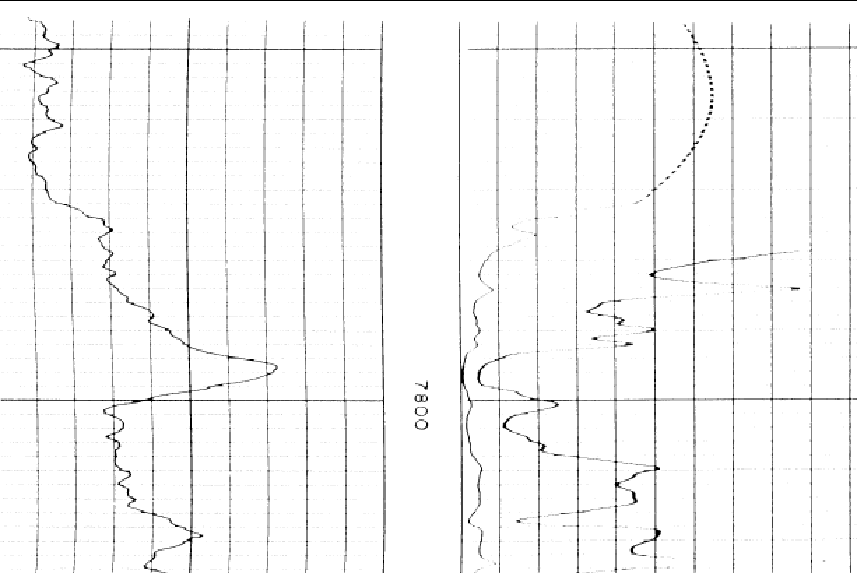
The original image (left) and after using the "Rotate Image" tool (right) Flip Black and White This tool flips the colors of the loaded image. For monochrome images, this will simply flip the black and white. Note that this tool will also flip the colors of color images as well. To use this tool, select Edit>Flip Black and White on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool.
The original image (left) and after using the "Flip Black and White" tool (right) Crop at EdgesThis tool removes the image file beyond the "Left-Most Edge" and "Right-Most Edge" in blue. To use this tool, select the
The original image with blue edge markers (left) and after using the "Crop at Edges" tool (right) Crop at DepthsThis tool removes the image file beyond the uppermost and lowermost depth calibration points, header, footer, or scale markers. To use this tool, select the Cut Out SectionThis tool removes a part of the image file between a user-selected top and bottom. Petra will automatically splice the image back together to form a continuous image. To use this tool, select Edit>Cut Out Section on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool. Next, set the top and bottom of the section to remove from the image. Note that Petra will add a blue box and outline over the selected area. Next, select "OK" to remove the section.
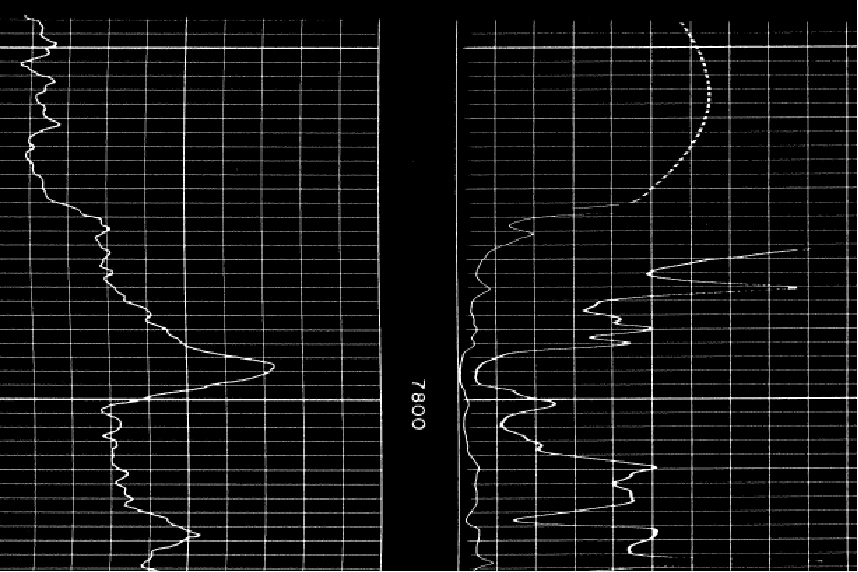
The original image with the top and bottom set in blue (left) and after using the "Cut Out Section" tool (right) Auto Trim EdgesThe Auto Trim Edges tool attempts to automatically remove blank space around the image. Manually using the "Crop at Depths" and "Crop at Edges" tool is often better, but slower. To use this tool, select Edit>Auto Trim Edges on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool. Remove Vertical LinesThis tool attempts to filter out vertical lines from the images. This tool works best on straightened images where the vertical lines are perfectly straight. Even slightly curved vertical lines won't be recognized by this process. To use this tool, select Edit>Filter>Remove Vertical Lines on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool.
The original image (left) and after using the "Remove Vertical Lines" tool (right) Remove Horizontal LinesThis tool attempts to filter out vertical lines from the images. This tool works best on perfectly horizontal lines. To use this tool, select Edit>Filter>Remove Horizontal Lines on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool.
The original image (left) and after using the "Remove Horizontal Lines" tool (right) De-Speckle ImageThis tool attempts to remove isolated dark spots on the image. To use this tool, select Edit>Filter>De-Speckle Image on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool. Enter the maximum dot size in pixels and select "OK." A smaller "Maximum Dot Size" setting will be more conservative, while a larger setting will remove more dots.
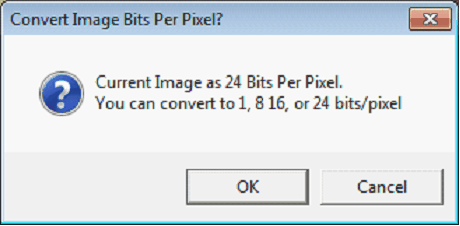
The original image (left) and after using the "De-Speckle Image" tool (right) Color to MonochromeSome raster images are saved as color files, even though they are scanned copies of black and white paper logs. This tool will convert color images to monochrome, which can decrease file size. To use this tool, select Edit>Color To Monochrome on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool. Convert Image Bits per Pixel"Color depth" indicates the number of bits that describe a single pixel's color in an image file. This is usually expressed in bits per pixel: 1 (monochrome), 8 (8-bit color) , 16 (high color), or 24 (true color) bits per pixel. Higher color depths represent finer color gradation, but take up more file space. Generally, raster images don't need high color depth to represent lithology. Note that this tool will only work on images with color depths above 1. To use this tool, select Edit>Convert Image Bits per Pixel on the menu bar at the top of the Raster Image Calibration tool.
|
 button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select
button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select 
 button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select
button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select 

 button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select
button on the toolbar. Alternatively, select